The Link Between Obesity and Diabetes: The Second Chapter
The problems of obesity and diabetes have become as major an issue as they have been in contemporary times. The complex interaction of these two conditions has to be appreciated if effective strategies for prevention and control are to be devised. Type 2 diabetes, in which the body becomes resistant to insulin or does not produce sufficient insulin, is greatly influenced by obesity, which is defined as the excessive accumulation of body fat. This review seeks to investigate and highlight the different facets of the relationship between obesity and diabetes. It will consider their features, specialties, uses and applications, main themes, advantages and disadvantages, and common questions asked.
Obesity and Diabetes: The Relationship
The relationship between and obesity and diabetes is not one-sided, but rather include various physiological factors, biochemical factors, and lifestyle aspects. Here are some of the key features of this link: Obesity
1. Insulin Resistance
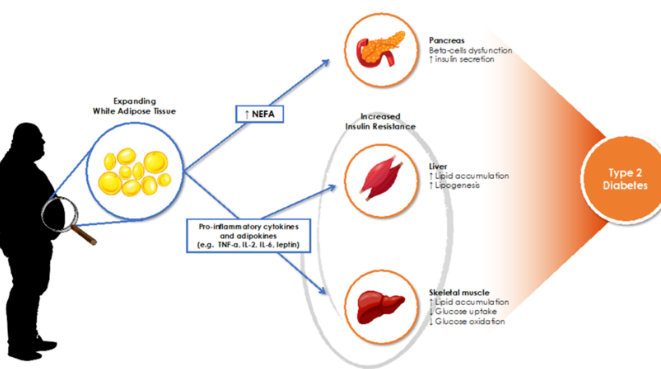
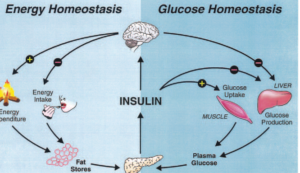
Insulin resistance is one of the major disease matrices that interconnects two diseases, obesity and diabetes. As obesity is generally defined as an excessive accumulation of body fat, obesity particularly second or visceral fat accumulation (abdominal fat) is deemed to interfere with proper functioning of insulin action in the body system. This creates a resistance that is a precursor of diabetes and leads to having high blood sugar levels evidenced by diabetes type 2.
2. Chronic Inflammation
Chronic low-grade inflammation is typical of obesity which can result in insulin resistance. Adipocytes or the fat cells secrete harmful inflammatory factors that can potentially impair normal metabolism of the body systems. This inflammation also worsens the condition of insulin insensitivity, while at the same time also contributing to the onset of diabetes-related complications.
3. Hormonal Changes
Obesity causes endocrine alterations that can make the interplay between these two conditions even worse. Leptin, a hormone that is involved in energy regulation, increased with the increase of fat deposits while adiponectin, an insulin sensitizing hormone, had low levels. This alteration in the hormonal levels may propel the development of diabetes.
4. Metabolic Syndrome
The association between obesity and diabetes is observed as well in the metabolic syndrome: a constellation of clinical conditions associated with increased risk of heart and vascular disease, and diabetes. People with metabolic syndrome usually have central obesity, elevated blood pressure, hyperglycemia and dyslipidemia.
5. Genetic Predisposition
Obesity and diabetes are resultants of both environmental and genetic factors. Variants of specific genes have been identified that raise the chances for obesity as well as Type 2 diabetes, revealing that a segment of the population is genetically influenced to be more vulnerable.
Specialty of The Link Between Obesity and Diabetes
What is unique about the linkage of obesity and diabetes is the fact that both conditions cannot be treated separately, and an interdisciplinary approach is required to combat both conditions. Here are several specialized areas that contribute to our understanding and management of this link:
1. Nutrition and Dietetics
Adverse eating habits are well known precursors of obesity and diabetes, the conditions rather need no introduction. We have nutritionists and dietitians who come to the frontline to inform individuals on what is reasonable to eat, how much to eat and when to eat it as well as the need for meal balance.
2. Endocrinology
Competition for resources is fierce. Endocrinologists are concerned with the management of disease facilitating hormones such as obesity or diabetes and how they operate within the body. Their main concentration is how such diseases can develop due to hormonal irregularities and therefore cause insulin sensitivity as well as dysfunction in metabolism.
3. Exercise Physiology
The management of obesity and diabetes goes well beyond nutrition and includes physical activity as well. Exercise physiologists specialize in preparing exercise plans for their clients with an objective to reduce weight, enhance sensitivity of insulin as well as improve general metabolism.
4. Behavioral Health
Psychology and counselling are key component in curbing the behavioral aspects of Obesity as well as Diabetes. They interact with the people and help them lower their emotional stress, substitutes such as emotional eaters and other psychological influences that make people become overweight and result in negative lifestyle choices.
5. Public Health
Such programs focus on the community approaches to the reduction of the obesity level and the prevention of diabetes; promoting active lifestyles, availability of healthy and qualitative foods and increase in physical exercises in different areas.
The Applications of The Relation of Obesity In Relation to Diabetes
The relation of Obesity to Diabetes has practical relevance in several spheres:
1. Prevention Programs
Understanding the relationships between these conditions makes it possible to tailor prevention programs. Such measures are aimed at lowering obesity prevalence so that the incidence of Type 2 diabetes may also be lowered. Community outreach, Education and school programs are efficient strategies.
2. Clinical Guidelines
Healthcare professionals understand this relationship and apply it in respective clinical guidelines. This enables them to know who to screen and how to manage obesity and diabetes. If such patients are detected early enough, it would be possible to take measures that prevent the development of diabetes.
3. Patient Education
Patients who are educated on how obesity relates to diabetes are motivated to change their behavior for the better. People are driven to such behavior because they understand how weight control can impact chances for getting diabetes.
4. Research and Innovation
The cause and effects junction between obesity and diabetes fuels some studies that attempt to establish the cause and effect relation in the first instance. This kind of research facilitates new treatment modalities, drugs, and technologies that enhance the management of the patient.
5. Policy Development
At a higher level, knowledge of this connection also shapes public policy from healthcare, nutrition and physical activity perspectives. Policy makers can introduce policies that promote the consumption of healthy foods, increase engagement in physical activities and support the management of weight through programs
Main Theme of The Link Between Obesity and Diabetes
The tight interrelationship that exists between obesity and diabetes hinges on prevention and management. This connection makes it clear that obesity has to be identified as a potential risk factor for Type 2 diabetes. Through diet and increased physical activity, many individuals are able to modify their lifestyles and thereby lower their risk for developing diabetes considerably.
1. Lifestyle Modifications The first mode entails introducing recommended lifestyle alterations such as exercise routines and nutritional practice within a milieu targeted at reducing both obesity and diabetes. These adjustments are permanent and will result in weight reduction, increased insulin sensitivity, and overall improved health.
2. Holistic Approach A balanced diet coupled with regular exercise is fundamental to any prevention or management plan of the patient at hand. Paying special attention to the emotional state of the person, their ability to procure healthy food, and their social network, will also make a difference
3. Collaboration Across Disciplines The first approach has call in for cooperation of different healthcare specialists with a view of finding a solution to the existing relationship between obese and diabetes. This approach helps in providing the individuals health care that is personalized to meet their needs.
Pros and Cons of The Link Between Obesity and Diabetes
Pros Cons 1. Awareness of Health Risks
1. Stigmatization of Obesity One of the benefits presented in this understanding is elevating the measures of health risks likely to be caused by obesity coupled with diabetes and factors relating them together. The relationship might be negative leading to stigmatization of those who are seen or are affected by the condition. 2. Improved Treatment Options
2. Complexity of Management Just understanding this relationship makes it possible all practitioners on the health care setting to design their programmed around the patients as per needs. It’s the case of having at hand both obesity and also diabetes which at times can be burdensome and need a series of approaches which take time.
3. Improved Research Opportunities 3. Misinformed Ideas
Given the association, researchers are engaged in studies that can develop new treatment approaches or preventive measures. Misinterpretations regarding the connection may foster misconceptions, which may make it more difficult to educate patients.
4. Changes in Policy 4. Constraints on Resources
If we increase understanding, we may also induce changes in public policies that will result in prevention of obesity. Insufficient availability of resources and lack of programs among poor can serve as barriers to effective prevention and control.
5. Education as a Means of Empowerment 5. Psychosocial Effects
Having knowledge about health enables people to be more aware and responsible over their weight and take measures to prevent diabetes. The psychological impact of obesity and diabetes is such that the affected individuals may suffer from depressive and anxious disorders.
Conclusion: The Adiposity and Diabetes Spectrum
This association of obesity with diabetes is fast becoming an area of interest in public health, practice, and research. To see this relationship is to consider obesity as a major contributor for the risk of developing type 2 diabetes. Through lifestyle changes, patient education, and team-based efforts, many individuals’ risks can be lessened and their health improved. As understanding increases and approaches change, the battle against obesity and diabetes remains pertinent in health enhancement and wellness.
Interlinkage Between Obesity And Diabetes – Most Commonly Asked Questions
What is the relationship between obesity and blood sugar levels?
Having excess body fat will, in the long run, induce insulin resistance and thus the body fails in the regulation of blood glucose levels. Raised levels of fat will prevent insulin from functioning normally and therefore raising blood sugar levels.
Does obesity induce Type 2 Diabetes? Can losing weight reverse this condition?
Yes, weight loss facilitates the improvement of insulin sensitivity and Type 2 diabetes can be reversed in some patients. It is significant to highlight here that a small weight loss of about five to ten percent can improve blood sugar levels.
What are the early symptoms of diabetes in obese people?
Being thirsty more than normal, urinating more than once, feeling tired more than necessary, and the most important is the blurriness of the vision. These symptoms are dangerous and It is important for obese patients to keep the red flag on them and take instruction from the healthcare providers.
Are there specific anti-obesity or diabetes medications to help control these diseases?
Yes, drugs that treat diabetes and that cause an advantage in weight loss are now available for example GLP-1 receptor agonist. These are in reality known as antidiabetic medications which tend to reduce insulin levels.
Where can I look for help when attempting to lose weight and control diabetes?
There are numerous options such as medical practitioners, dieticians, support groups, communities and websites that offer information’s and ideas on weight control and diabetes management.